Electronic components
Electronic components can be classified in:
- Active components: usually can inject power into a circuit. They are made of semiconductors. E.g: Diodes, transistors.
- Passive components: cannot introduce net energy into the circuit. E.g: Resistors, capacitors
For a circuit to be properly called “electronic circuit” it must contain at least one active element.
Passive components
Fixed resistors
- They impede the flow of electric current
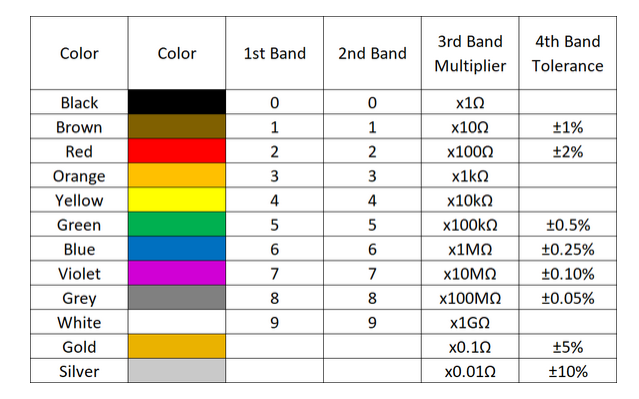
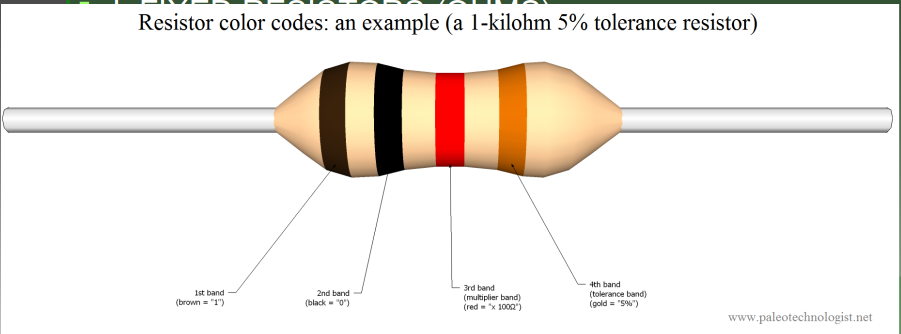
- There is a colour code to know their value
Variable resistors
- Potentiometer: A potentiometer is a three-terminal resistor with a sliding or rotating contact that forms an adjustable voltage divider.
- Thermistor: semiconductor type of resistor whose resistance is strongly dependent on temperature. They can be
- Negative-temperature-coefficient (NTC): thermistors have less resistance at higher temperatures
-
-
- Positive-temperature-coefficient (PTC): thermistors have more resistance at higher temperatures
-
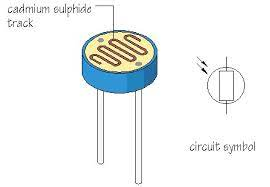
- Light Dependent Resistors (LDR): passive component that decreases resistance with respect to receiving luminosity on the component's sensitive surface
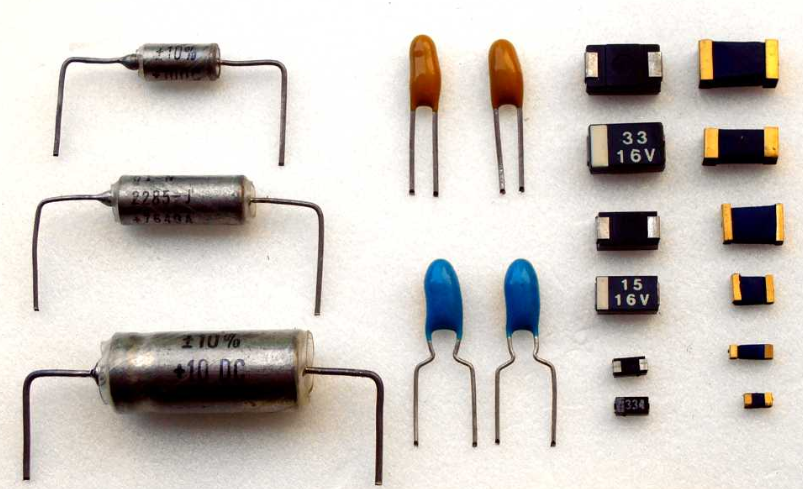
Capacitors
Device that stores electrical energy by accumulating electric charges on two closely spaced surfaces that are insulated from each other.
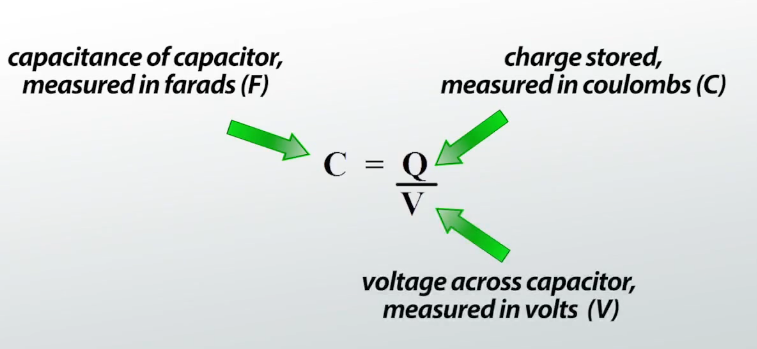
The property of a capacitor is the capacitance (C) that is defined as the amount of charge that can be stored at a given voltage. It is measured in Farads (F)
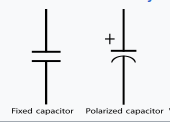
Electronic symbol
Active components
They are made up of semiconductor materials, whose properties allow to introduce "control" in the circuit.
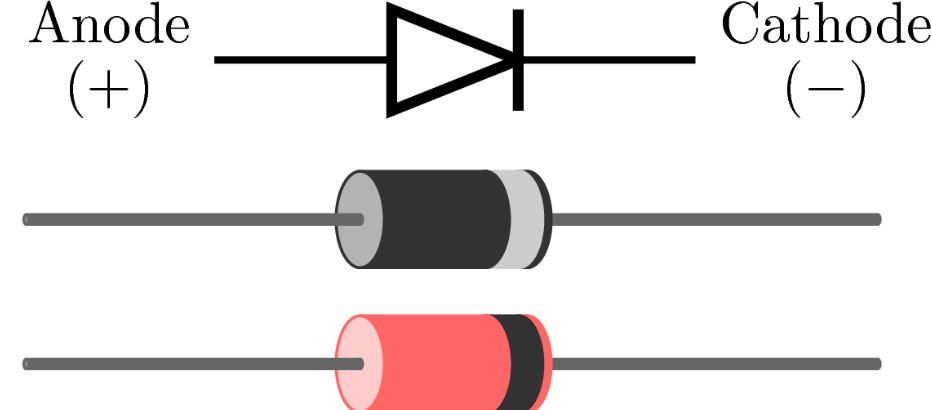
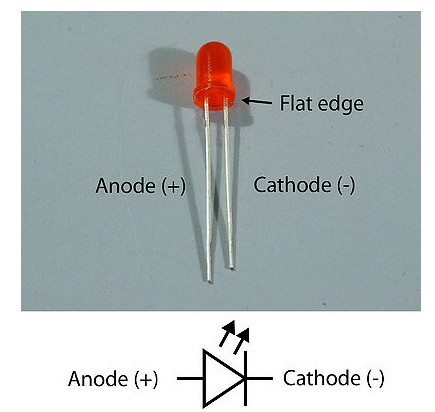
Diodes
Devices that allow current to flow just in one direction.
The most known are LED's: Light Emitting Diode
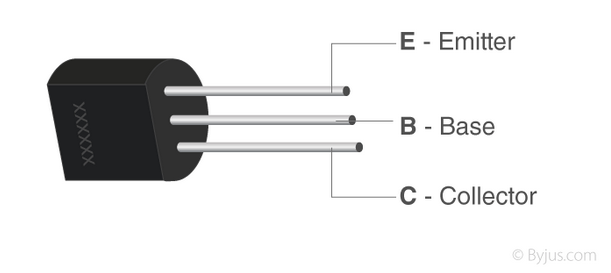
Transistors
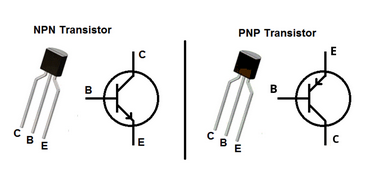
It is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electrical signals and power. It is composed of semiconductor material, usually with at least three terminals for connection to an electronic circuit. A voltage or current applied to one of the transistor's terminals (Base) controls the current through another pair of terminals (Collector and Emitter)
There are two main types of transistors depending on the sense of the controlled current: NPN and PNP
Information and images extracted from:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronic_component
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Capacitor
- https://study.com/academy/lesson/capacitance-units-formula.html
- http://cmra.rec.ri.cmu.edu/products/electronicsv2/basic_components/what_is_an_led/1/vid1.html
- https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transistor
- https://byjus.com/jee/transistor/
- https://shoptransmitter.com/blog/what-is-the-difference-between-pnp-and-npn/




No comments to display
No comments to display