Introduction
What is programming?
Programming is providing the necessary instructions to a machine or device so that it can work automatically.
In every program there are a series of elements that will always be present:
- Input: data or information that must be provided to the machine so that it can perform the desired operations.
- Ouput: information or result that the machine shows.
- Storage: The data, while being processed by the machine, needs to be stored in some way to work with it. Here we will talk about variables, vectors, matrix or other complex data storage structures, although in this course we will limit ourselves to working with variables.
- Processing: operations to which the data is subjected to obtain the desired results. They can be arithmetic, logic, loops, conditionals, etc...
The development of a program consists of the following steps:
- Definition and analysis of the problem
- Algorithm design using flowcharts.
- Program coding: obtaining the source code using the chosen programming language.
- Compilation: conversion of source code to machine language.
- Bug debugging and program checking.
- Operation: documentation and maintenance. In this course, due to the simplicity of the programs created, we will not go into this step, although it is essential that every good program be accompanied by good documentation and a good update plan.
There are a series of principles when designing software that are common:
- KISS: acronym for Keep It Simple, Stupid! This principle tells us that any system will work better if it is kept simple than if it becomes complex. Simplicity has to be a goal in development and unnecessary complexity must be eliminated.
- DRY: acronym for Don't Repeat Yourself. This principle talks about the duplication of the code, first of all because of the previous principle, and also because subsequent maintenance becomes more difficult since we do not know where we have to modify things because they are repeated on various occasions throughout the program and the inconsistencies multiply.
For further information about these principles consult here.
Flowcharts
An algorithm is a sequence of steps that must be performed to solve a problem.
A flowchart is a way to represent a process or algorithm in a visual, structured and organized way. It is a very useful tool to organize and structure a programming task before jumping directly into the code.
Example of flowchart:
There are various computer programs for creating flowcharts. Most text processors or slideshow software allow it. However, it is advisable to create flowcharts first with paper and pen, and if appropriate in a collaborative way, and use the software to simply edit them finally to include as program documentation.
Elements of a flowchart
A flowchart is fundamentally made up of the following elements:
- Flowline: Shows the process order of operation. It is a line coming from one symbol and pointing at another
- Terminal: Indicates the beginning and ending of a program or sub-process. Represented as an oval or rounded rectangle. They usually contain the word "Start" or "End"
Process: Represents a set of operations that changes value, form, or location of data. Represented as a rectangle.
- Input data: Indicates the reception of data at the input. It is represented by a rhomboid and an inward arrow.
- Output data: Indicates printing data on output. It is represented by a rhomboid and an arrow pointing out.
- Decision: Shows a conditional operation that determines which one of the two paths the program will take. The operation is commonly a yes/no question or true/false test. Represented as a diamond.
- Other: Like some types of loops, we will see them later.
Simple examples of flowcharts
Example 1: Flowchart of a program that takes two numbers, adds them and shows the result on the screen
SOLUTION:
- Output: It must ask for the two numbers to add, and then show the result.
- Input: the two numbers to add
- Storage: two variables to store the two numbers (num1 y num2) , and a third one to store the result (result)
- Processing: Addition.
Flowchart
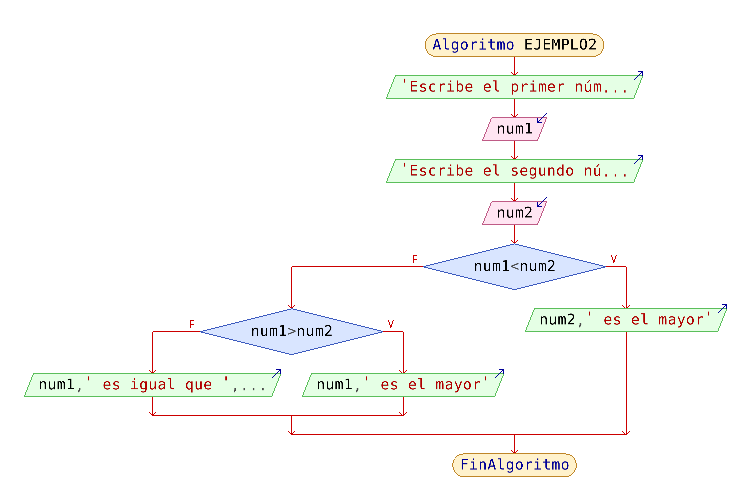
Example 2: Flowchart of a program that compares two numbers which is larger and displays it on the screen.
SOLUTION:
- Output: it must ask the two numbers to compare and then show the result of the comparison.
- Input: the two numbers to compare
- Storage: two variables to store the numbers to compare (num1 y num2)
- Processing: logic comparison.
Flowchart: